Endometrial Polyps
At Mamata Fertility Hospital in Secunderabad, we’re dedicated to providing patients with thorough and easy-to-understand knowledge about their health.
Endometrial polyps can affect many women, and understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is the first step to feeling empowered and reassured.
This guide goes beyond basic information to provide detailed insights into managing and treating this condition.
For Appointments, Please Call:
More On Low Sperm Motility
What are Endometrial Polyps?
Imagine the inside of your uterus as a lush garden. The inner lining, called the endometrium, thickens each month as part of your body’s natural cycle. However, sometimes this lining grows in an unbalanced way, leading to small, mushroom-like growths called endometrial polyps. These can range in size, from as tiny as a sesame seed to as large as a golf ball.
Though most polyps are non-cancerous, they can cause bothersome symptoms like bleeding or fertility challenges. Rarely, they may become cancerous, underscoring the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment.
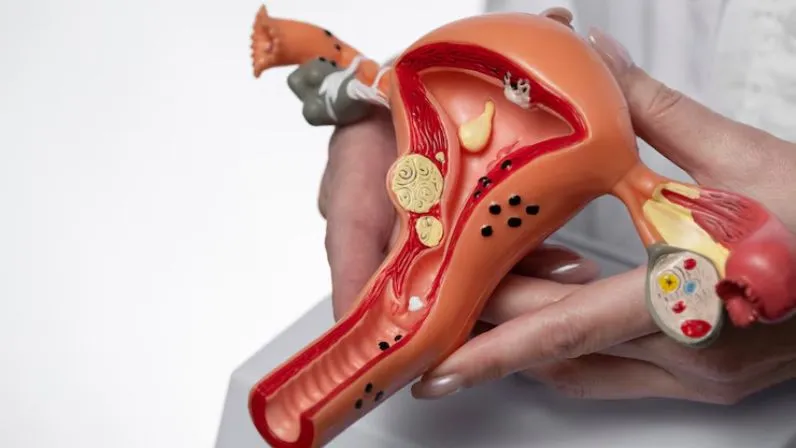
Causes and Risk Factors
What Causes Endometrial Polyps?
Endometrial polyps develop when there is an overgrowth of cells in the uterine lining, often triggered by hormonal changes. The hormone estrogen, in particular, plays a key role in regulating the growth of the endometrial lining. Excess estrogen or an imbalance between estrogen and progesterone can cause this overgrowth.
Key Risk Factors
While anyone with a uterus can develop polyps, certain factors increase the likelihood:
- Age and Hormones
- Women in their 40s and 50s, particularly those nearing menopause, are more likely to develop polyps. This is often linked to increased hormonal fluctuations during this stage of life.
- Obesity
- Excess body fat raises estrogen levels, which could lead to irregular growth in the uterine lining. Studies show that women with higher Body Mass Index (BMI) are at greater risk.
- Use of Medications
- Certain medications, like tamoxifen (used for treating breast cancer), can increase the odds of developing polyps as a side effect, promoting endometrial tissue growth.
- Underlying Medical Conditions
- Women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or chronic illnesses like diabetes or hypertension often face a greater risk, likely due to associated hormonal imbalances.
- Genetic or Reproductive Factors
- Women who have never been pregnant or those with a family history of uterine issues are also at a slightly higher risk.
Understanding these risk factors can help you discuss preventive measures with your gynecologist and take early action when needed.
Endometrial Polyps, Pregnancy & Fertility
Endometrial polyps are an important consideration for women who are trying to conceive or are already pregnant. These growths in the uterine lining can sometimes affect fertility and pregnancy, but with proper care and treatment, most women can achieve their desire for a healthy pregnancy.
How Endometrial Polyps Affect Fertility
For women trying to get pregnant, endometrial polyps can sometimes present challenges. Here’s how they may influence fertility:
- Interference with Embryo Implantation:
- The endometrium (uterine lining) is where a fertilized egg implants itself to begin a pregnancy. Polyps may disrupt this process by acting as a physical barrier or by altering the environment of the uterine lining, making implantation difficult.
- Inflammation Issues:
- Polyps can cause local inflammation in the uterus, which might reduce the chances of implantation or create an environment not ideal for pregnancy.
- Hormonal Effects:
- If polyps are connected to hormonal imbalances (like excessive estrogen), this may indirectly impact ovulation and overall fertility.
Studies suggest that removing endometrial polyps through a procedure called hysteroscopic polypectomy often significantly improves fertility outcomes, particularly for women undergoing fertility treatments like IVF.
Endometrial Polyps During Pregnancy
If you’re already pregnant and diagnosed with endometrial polyps, it’s natural to have concerns. While these growths are usually benign, they do require monitoring. Here’s what you should know:
- Bleeding During Pregnancy:
- Endometrial polyps can sometimes cause spotting or bleeding during pregnancy. This is often due to increased sensitivity in the uterine lining. While distressing, this symptom is typically not dangerous for the baby.
- Impact on Placenta or Delivery:
- Rarely, large polyps might affect the attachment of the placenta or increase the risk of complications during labor and delivery. However, such cases are uncommon, and doctors usually monitor and manage the situation effectively.
- Increase in Size:
- Pregnancy hormones, especially estrogen, might stimulate the growth of existing polyps, leading to further monitoring.
How Endometrial Polyps Are Managed
At Mamata Fertility Hospital, your health and the safety of your pregnancy are our top priorities. Here’s how we support women with endometrial polyps:
- Before Pregnancy:
- If you’re trying to conceive and polyps are detected, your doctor will likely recommend removal to maximize your fertility chances.
- During Pregnancy:
- Most of the time, polyps are simply observed during pregnancy. Unless a polyp is causing significant bleeding or other complications, interventions are avoided during this critical time. Doctors may recommend regular ultrasounds to monitor the polyp’s size and any associated effects.
- After Pregnancy:
- If a problematic polyp is diagnosed during pregnancy but doesn’t cause immediate concerns, it can be addressed after delivery. This ensures minimal disruption to your pregnancy.
Reassurance for Expecting Mothers
It’s reassuring to know that most women with endometrial polyps can have healthy pregnancies. With the right care and monitoring, complications are rare and manageable. If you are experiencing symptoms like abnormal bleeding or difficulty conceiving, consult our experts at Mamata Fertility Hospital for guidance tailored to your needs. Together, we can help you achieve your dream of starting or growing your family, with solutions designed just for you.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing Symptoms
Endometrial polyps don’t always cause noticeable symptoms, which is why some cases are only detected during routine check-ups. However, symptoms may include:
- Irregular Bleeding: Spotting or bleeding between periods, heavy menstrual flow, and unpredictable cycles.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Any bleeding after menopause should be immediately evaluated by your doctor.
- Difficulty Getting Pregnant: Polyps can act like a physical barrier, obstructing the uterine cavity and affecting embryo implantation.
- Pelvic Pain or Discomfort: Though uncommon, some women report vague cramps or pressure in the lower abdomen.
If you experience these symptoms, do not ignore them. Early intervention can help prevent complications and ensure better outcomes.
How Are Polyps Diagnosed?
Doctors at Mamata Fertility Hospital use advanced and reliable methods to diagnose polyps accurately. Here’s what you can expect during your visit:
- Ultrasound (Transvaginal):
- This non-invasive imaging test provides a close look at your uterus and can help identify suspicious tissue growths.
- Sonohysterography:
- Saline is injected into the uterine cavity to give clearer ultrasound images, enabling your doctor to detect even smaller polyps.
- Hysteroscopy:
- A tiny camera is introduced into the uterus for direct visualization of the polyps. This is often combined with a biopsy for a more definitive diagnosis.
- Endometrial Biopsy:
- Small tissue samples are collected and examined under a microscope to rule out or confirm cancerous changes.
These advanced diagnostic tools make it possible to detect and address polyps effectively, often during a single visit.
Lifestyle and Support Recommendations
While medical treatments are vital, your everyday choices also play a significant role in managing endometrial polyps and improving overall health. Here are practical tips:
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Dietary Changes:
- Include foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds. These foods not only balance hormones but also support immune function.
- Regular Exercise:
- Physical activities like yoga, walking, or swimming help maintain a healthy weight and stabilize hormones, reducing risk factors tied to obesity.
- Stay Hydrated:
- Adequate water intake aids in overall metabolic and hormonal function.
Emotional and Psychological Support
- Talk to Experts:
- Your gynecologist or fertility specialist can guide you through emotional challenges or stress related to symptoms or fertility concerns.
- Join Support Communities:
- Connecting with others who’ve faced similar challenges can reduce feelings of isolation and offer comfort.
Preventive Check-Ups
Make routine screenings a part of your health plan, especially if you’re nearing menopause or have experienced unusual symptoms.
Treatment and Management Options
Individualized Care Plans
Treatment plans depend on factors like the size and number of polyps, symptoms, and whether or not you’re trying to conceive.
Non-Surgical Approaches
- Watch and Wait:
- Small, asymptomatic polyps often require no immediate action. Regular monitoring ensures prompt treatment if needed.
- Hormonal Therapies:
- Medications like progestins or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists help manage excessive endometrial growth, but they are often temporary solutions.
Surgical Options
For more significant or symptomatic polyps, surgery may be recommended:
- Polypectomy:
- This is the most common treatment, performed using hysteroscopy. The procedure is minimally invasive and has a quick recovery time, usually allowing you to go home the same day.
- Endometrial Ablation:
- This method removes the uterine lining entirely and is generally recommended for women who are not planning future pregnancies.
- Hysterectomy:
- Reserved for severe cases where the risk of recurrence or malignancy is high, this involves the complete removal of the uterus.
At Mamata Fertility Hospital, we make sure each procedure is tailored to your specific needs, whether you’re managing symptoms or looking to preserve fertility.
FAQs
1. Do all endometrial polyps require treatment?
Not always. If polyps are small and symptomless, doctors may suggest monitoring them closely rather than intervening immediately.
2. Can polyps cause infertility?
Yes, polyps can sometimes block the uterine cavity or make it difficult for the embryo to implant. Removing polyps often boosts fertility prospects.
3. Is surgery painful?
Polyp removal via hysteroscopy is minimally invasive and generally pain-free. Most patients recover quickly, with little to no discomfort.
4. Do polyps grow back after removal?
Polyps can recur in some cases. Regular follow-ups and a healthy lifestyle can help in early detection and prevention.
5. When should I see a doctor?
Visit your doctor immediately if you experience irregular bleeding, postmenopausal spotting, or difficulty conceiving. Prompt diagnosis ensures safer outcomes.
At Mamata Fertility Hospital, your health is our priority. If you suspect endometrial polyps or have any related concerns, reach out to us for expert, compassionate care. Together, we can create a health plan tailored to your needs and ensure peace of mind for a healthier tomorrow.
Reviewd By

Dr Aarti Deenadayal Tolani
Clinical Director, Scientific In-Charge & Fertility Consultant
MBBS, MS ( OBGYN), FICOG
Expert in Reproductive Endocrinology, Infertility, Advanced Gynaec Ultrasound, and Faculty at Mamata Fertility Hospital.
Blogs and Articles

Miscarriage Risk by Week and Age
Learn miscarriage risk by week and age, causes, signs, and prevention tips. Get expert care from Mamata Fertility Hospital Hyderabad.

Irregular Periods During Breastfeeding: Causes, Symptoms & When to Seek Help
Breastfeeding can cause irregular periods due to hormonal changes. Learn why this happens, when to expect your cycle to return, and when to seek medical advice.
Does PCOS Cause Infertility? Causes, Treatment & Pregnancy Chances
PCOS can affect fertility, but pregnancy is possible with treatment and lifestyle changes. Learn how to manage PCOS and improve your chances of conception.

